The seductive power of music is, many might agree, a largely undiscovered realm: those mystical combinations of melody, harmony, and rhythm that have the power to stir emotions and transport listeners to otherworldly realms. One such combination, the Lydian Mode, stands as a testament to the profound influence of ancient theoretical constructs over modern musical landscapes, particularly in the realm of film music. This construct, rooted in the music theory of the ancient Greeks, imparts an ethereal, dreamy quality to compositions which has not lost its allure over the centuries and has found a fitting home in the soundtracks of modern Hollywood.
“The Lydian mode creates a ‘spacey’ sound. It’s often used to depict otherworldly moments or to communicate the vastness of space or the depth of an ocean.”
Michael Miller, Music Theory for Dummies
The Lydian mode is easily spotted in notable Hollywood scores. The heart-wrenching main theme from E.T. The Extra-Terrestrial and the iconic fanfare from Superman are popular examples of the application of the Lydian mode in film music. The table below provides additional examples of such incorporation:
| Film | Composer | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Star Trek | Jerry Goldsmith | Main Theme |
| Edward Scissorhands | Danny Elfman | Main Title |
| Harry Potter Series | John Williams | Hedwig’s Theme |
The aim of this article is to delve into the enchanting world of the Lydian mode, its history and unique characteristics, and to explore its influence in film scores. We also aim to provide useful tips for composers interested in crafting Hollywood-style music while maintaining the essence of the Lydian mode. The hope is that composers, musicians, and music enthusiasts alike find these insights intriguing and revealing of the pervasive influence of this ancient mode in the evocative realm of film music.
Exploring the Origins of the Lydian Mode
The Lydian mode’s historical contributions to film music are vast and undeniable, with its roots dating back to the Renaissance era. Over the centuries, its special qualities were recognized and found particularly effective in conveying an array of differing atmospheres, from the surreal to the ecstatic, thus working beautifully to augment the storytelling potency of films.
One of the earliest known instances of the Lydian mode’s use in the world of music extends back to the sacred music of the Middle Ages. Here, plainsong or ‘Gregorian Chant’ as it’s largely known, explored a multitude of modal scales, with the Lydian mode being one of the dominant ones used in compositional design. The unique tonal qualities offered by the Lydian mode were indeed conducive to these hymn-like melodies, beautifully conveying the sense of devotional fervor characteristic of religious music during this era.
“The Lydian mode marries mysticism with mellifluity in a way that could hardly be more complimentary to the emotive intentions of a film’s soundtrack.“
As the progress of musical theory evolved, so did the use of the Lydian scale. By the Baroque and Classical eras, it was transforming from a strictly liturgical modality into a secular one. It became widely embraced by the composers of these periods, becoming integral to their compositions, lending vibrancy to melodies and invigorating harmonies.
However, it was during the 20th century, with the emergence and rapid growth of film industry, the Lydian mode found its true calling. The silver screen became a platform where composers could experiment freely with this particular mode. Its naturally cinematic quality combined with its distinct knack for invoking an array of emotions, proved invaluable to their composition. Film scores were no longer just accompaniments; they became an integral part of the storytelling. And composers, encouraged by the Lydian mode’s flexibility and emotive power, incorporated it into their work with stunning regularity and finesse.
From the time of its earliest use in Gregorian chants to its incorporation in modern film scores, the Lydian mode has always had an ethereal quality to it. Its distinctive sonic capabilities and its ability to affect mood and emotion have made it a popular choice for composers throughout history and continue to do so in contemporary film music. And while its application may have evolved over time, its essence remains the same – that of evoking profoundly expressive responses in the listener, thus enriching the cinematic experience.
The Unique Characteristics of the Lydian Mode
The Lydian mode, beloved by Hollywood composers, carries a dreamy, otherworldly quality, and a disproportionately strong presence in science fiction and fantasy film scores. Delving deeper into this exquisite tonality, the key distinction lies in its raised fourth scale degree. Unlike its cousin, the major scale (or Ionian mode), where the fourth degree is naturally formed, beguiling Lydian elevates it by a half-step, an alteration brimming with implications for composers crafting emotive film music.
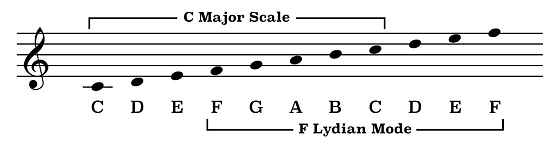
When exploring the Lydian mode, it’s important to illuminate its characteristic “Lydian sound”. This is often described as ‘bright’, ‘majestic’, or ‘ethereal’, as the raised fourth generates a constant pull towards resolution — a tension mirrored in compelling narratives harrowing en route their climactic turning points. Close your eyes, imagine the grandeur of the Middle-Earth in “The Lord of the Rings”, or feel the mysterious expanses of the universe echoing in “2001: A Space Odyssey”; the Lydian mode shapes the auditory landscape, mesmerizing and enchanting audiences far and wide.
The Lydian mode is significant in music theory because it is one of the few modes that contains a tritone, which is a highly dissonant interval. This dissonance can be used to create tension in a piece of music, and resolving this tension can create a powerful emotional effect. In addition to its use in creating tension, the Lydian mode is also often used to evoke a sense of mystery or otherworldliness. This is due to its ‘sharp’ sound, which can sound strange or exotic to Western ears. This makes it a popular choice for film scores, where it can help to create a distinctive atmosphere.
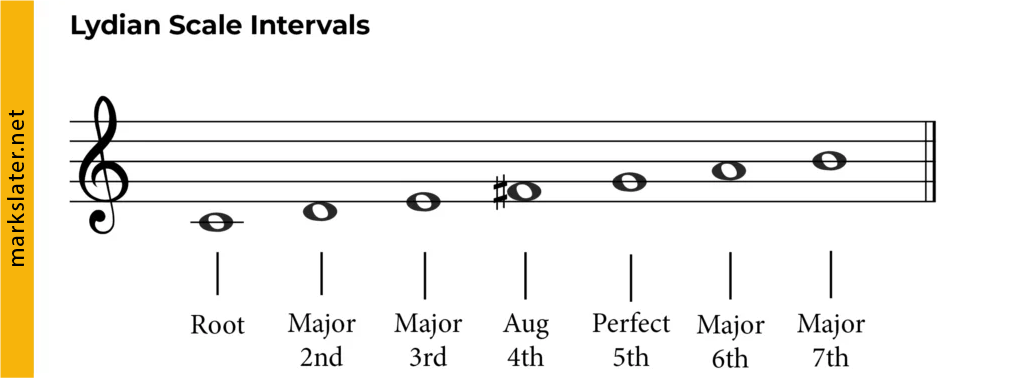
Practical Tips for Writing Film Music in the Lydian Mode
Once you understand the structure of the Lydian mode, you can start to experiment with chord progressions. The most common chord progression in the Lydian mode is I-II, which emphasizes the raised fourth. Other effective chord progressions include I-IV, I-vii, and ii-V. These progressions can be used to create a sense of tension and release, which is a key element of effective film scoring.
Melody writing in the Lydian mode can be a bit tricky, as the raised fourth can create a sense of dissonance if not handled correctly. One effective technique is to use the raised fourth sparingly, as a color note. This can create a sense of surprise and interest. Another technique is to use the raised fourth as a pivot note, transitioning from the Lydian mode to another mode or key. This can create a sense of movement and progression.
In addition to melody and harmony, rhythm and instrumentation are also important considerations when writing in the Lydian mode. The Lydian mode lends itself well to syncopated rhythms, which can add a sense of energy and excitement. In terms of instrumentation, the Lydian mode can be effectively used with a wide range of instruments, from strings and brass to synthesizers and percussion. The choice of instruments can greatly affect the mood and texture of the music.
Finally, it’s important to remember that the Lydian mode is just one tool in the composer’s toolbox. While it can be a powerful tool for creating a specific mood or atmosphere, it should be used in conjunction with other musical elements to create a cohesive and effective film score. Experimentation and creativity are key when writing in the Lydian mode.
Practical Tips for Writing Film Music in the Lydian Mode
1. Study the Masters
One of the best ways to learn how to write music in the Hollywood style is to study the works of renowned film composers. Take the time to listen to soundtracks from classic and contemporary movies, paying close attention to how the music enhances the storytelling. Analyze the harmonic progressions, melodic motifs, and orchestration choices to gain insights into the techniques used.
2. Understand the Emotional Arc
In film music, it’s crucial to understand the emotional arc of the story and how music can support and enhance it. Identify the key moments in the narrative and consider how the music can heighten the emotions experienced by the audience. Use harmonic progressions, instrumentation, and dynamics to create tension, suspense, or resolution where appropriate.
3. Experiment with Harmonic Progressions
Harmony plays a significant role in creating the Hollywood sound. Experiment with different chord progressions, including those that incorporate the Lydian mode. The raised fourth degree of the Lydian mode can add a touch of magic or mystery to your compositions. Combine it with other modes or scales to create unique and compelling harmonic progressions that capture the essence of the story.
4. Develop Strong and Memorable Themes
In Hollywood film music, memorable themes are often the backbone of the score. A strong and recognizable theme can help to establish and reinforce the emotional connection between the audience and the story. Spend time crafting melodies that are catchy, emotive, and reflective of the characters or settings they represent. Use motifs and variations to develop the themes throughout the film, creating a cohesive musical narrative.
5. Embrace Collaboration
Writing music for films is a collaborative process. Collaborate with directors, producers, and other members of the creative team to understand their vision and how the music can support it. Be open to feedback and revisions, as it’s essential to create a score that aligns with the overall artistic vision of the project.
Conclusion
The use of the Lydian mode in Hollywood movies has become synonymous with creating a sense of wonder, magic, and otherworldliness. By studying the works of renowned film composers and understanding the emotional arc of the story, aspiring composers can learn how to write music in the iconic Hollywood style. Experimenting with harmonic progressions, developing strong themes, and embracing collaboration are key elements in creating memorable film music that captivates audiences and enhances the cinematic experience.